Federated Infrastructure for Collaborative Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Environments
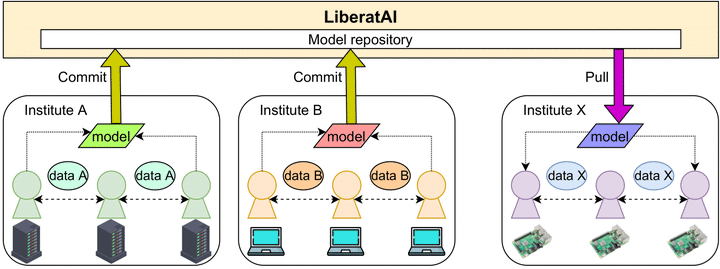 Architecture of Proposed Infrastructure
Architecture of Proposed Infrastructure
Federated learning is a technique for training machine learning models while keeping data private. The data is kept on the devices or servers where it was collected, and only updates to the model are shared between the parties involved in the training process. This approach is effective in addressing privacy concerns and allows for a diverse dataset, with data coming from multiple sources. However, resource constraints on edge devices make it difficult for all user devices to use the same model, which could impact the model’s accuracy. Enabling federated learning in heterogeneous environments is therefore essential for high model accuracy, given the importance of a large and diverse dataset to train the model effectively. When training or using machine learning models, the limitations of each heterogeneous client environment are taken into consideration. This article focuses on the heterogeneity of existing client hardware resources, including storage, computing, and communication. Despite this, there is currently no federated learning platform that considers the various limitations of heterogeneous environments on clients.
Design and Implementation
The proposed infrastructuer enables the collaborative development of machine learning models on heterogeneous environments while preserving data privacy. Users can train the model with their local dataset on their environments and share the trained model via the proposed infrastructure for aggregating the model with others from other developers or researchers. Federated learning is applied to train the models collaboratively by keeping the dataset on the client side to protect data exploitation. The model is exchanged between a server and clients instead of exchanging the raw data. Since edge devices have more computing power than ever, we can deploy and train the model on the client side. However, each environment has its own limitation so the proposed infrastructure provides the model and execution environment which is compatible with the existing client’s hardware environments.
Training models on the client side is not trivial because the limitation of client hardware needs to be considered. The proposed infrastructure is composed of three main modules: (1) compressor module to handle heterogeneous storage resources, (2) aggregator module to handle heterogeneous computing resources, and (3) sparsifier module to handle heterogeneous communication resources.
Evaluation
The proposed infrastructure was evaluated in a scenario to train models that detect COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. COVID-19 detection is a typical privacy-sensitive use case of machine learning because chest X-ray images may be used to identify patients and could lead to privacy violations
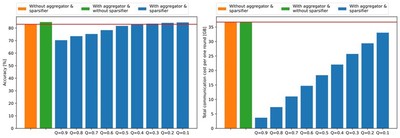
The figure shows the accuracy and communication cost for applying aggregator and sparsifier modules. As a result, the proposed infrastructure achieves higher model accuracy than federated learning of the models with homogeneous structure while consuming less communication cost.
Future Work
In the future, the generality of the proposed infrastructure will be investigated using a variety of machine learning applications with diverse structures of machine learning models. We plan to evaluate the proposed infrastructure on a large number of edge devices and then improve the resource utilization in the infrastructure. Additionally, we will make the proposed infrastructure as open-source software and available for the international or domestic research communities to remove the barrier to the collaborative development of machine learning models from the limitation of data privacy and existing resource constraints.
Publication
-
Kundjanasith Thonglek, Keichi Takahashi, Kohei Ichikawa, Chawanat Nakasan, Hidemoto Nakada, Ryousei Takano, Pattara Leelaprute, Hajimu Iida, “Automated Quantization and Retraining for Neural Network Models Without Labeled Data,” in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 73818-73834, Jul. 2022. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3190627
-
Kundjanasith Thonglek, Keichi Takahashi, Kohei Ichikawa, Chawanat Nakasan, Pattara Leelaprute, Hajimu Iida, “Sparse Communication for Federated Learning”, IEEE International Conference on Fog and Computing, May. 2022. DOI: 10.1109/ICFEC54809.2022.00008
-
Kundjanasith Thonglek, Keichi Takahashi, Kohei Ichikawa, Chawanat Nakasan, Hajimu Iida, “Federated Learning of Neural Network Models with Heterogeneous Structures”, IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Dec. 2020. DOI: 10.1109/ICMLA51294.2020.00120
-
Kundjanasith Thonglek, Keichi Takahashi, Kohei Ichikawa, Chawanat Nakasan, Hidemoto Nakada, Ryousei Takano, Hajimu Iida, “Retraining Quantized Neural Network Models with Unlabeled Data”, IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Jul. 2020. DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9207190